Understanding the Cash Flow Challenges in Global Trade
Managing cash flow effectively remains one of the most significant challenges for companies engaged in import and export. In many transactions, sellers ship goods well before receiving payment, while buyers may not receive products until weeks or months after settlement. This timing gap can place immense pressure on company finances, disrupt supply chains, and restrict the ability to grow. Leveraging financing tools from providers like trade finance Sydney is essential for businesses aiming to bridge this gap and facilitate smoother, more secure cross-border trade.
Without the safety net of trade finance, exporters are exposed to escrow and settlement risks, while importers face the challenge of paying for goods they have not yet received. In a climate where geopolitical volatility and logistics disruptions are increasingly common, closing the cash flow gap is crucial for protecting profit margins, sustaining operations, and maintaining relationships with trading partners.
The Role of Trade Finance in Bridging the Gap
Trade finance is a financial product suite designed to streamline and secure international commerce. These solutions range from advances on invoices to complex documentary credits and insurance products. The primary aim is to ensure that exporters receive prompt and guaranteed payment for goods shipped, while importers gain access to products without up-front cash outlays. In this way, trade finance supports the free flow of goods and capital, reduces non-payment risk, and increases trust between global buyers and sellers.
By combining various instruments, trade finance providers simplify cross-border dealings and help companies overcome working capital bottlenecks. Whether a business is scaling into new export markets or managing seasonal purchasing cycles, trade finance offers customized solutions tailored to each participant’s needs.
Key Instruments in Trade Finance
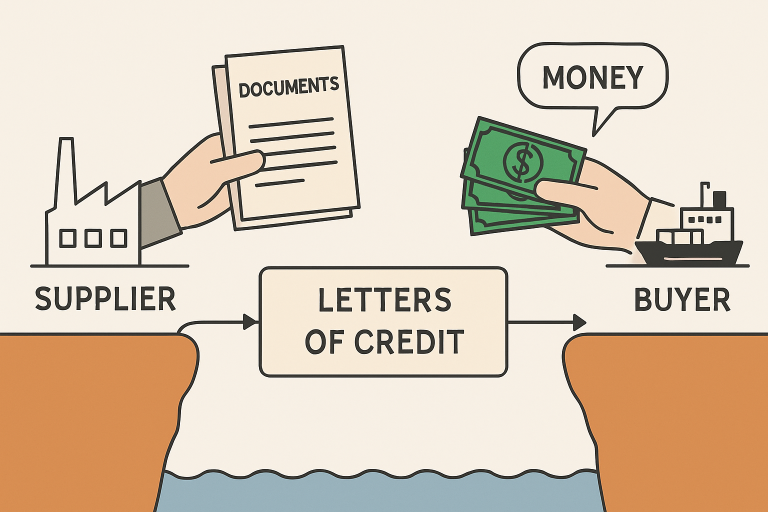
- Letters of Credit (LCs): These widely used guarantees ensure that payment is only released once sellers have fulfilled predetermined shipment and documentation terms. LCs provide mutual assurance to buyers and sellers, often essential in markets with high regulatory or credit risk.
- Trade Credit Insurance: This insurance coverage mitigates the risk of buyer non-payment due to insolvency or political unrest. It enables exporters to expand into new regions more confidently, knowing receivables are protected.
- Factoring: Suppliers can sell their accounts receivable to financial institutions at a discount, receiving immediate cash. This liquidity injection is especially valuable for SMEs operating on thin margins or with longer sales cycles.
Benefits for Buyers
For importers, trade finance unlocks several key benefits. Access to capital allows them to negotiate extended payment terms with suppliers, strengthening their bargaining power and preserving operational liquidity. Trade finance also helps buyers manage inventory levels, buffer against shipping delays, and smooth out procurement cycles. Additionally, risk mitigation tools embedded in trade finance products protect buyers against delivery defaults and quality disputes, making cross-border sourcing more predictable and less risky.
Advantages for Sellers
Exporters also stand to gain significantly from trade finance. Guaranteed payment mechanisms such as letters of credit or insured receivables protect them against counterparty risk, promoting confidence in entering new markets and onboarding new clients. This stability in cash flow allows suppliers to reinvest, fund research and development, and maintain healthy working capital. Invoice factoring and similar solutions foster a proactive approach to receivables management and minimize bad debt losses.
Addressing the Global Trade Finance Gap
Despite the wide array of available instruments, a massive trade finance gap persists around the globe. According to the Asian Development Bank, this gap reached $2.5 trillion in 2022, shutting out many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and companies in developing economies from full participation in world trade. Initiatives such as the $1 billion trade finance program launched by HSBC in partnership with the International Finance Corporation (IFC) are working to close this gap and expand access to funding for businesses across Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East.
Technological Innovations in Trade Finance
Digital transformation is changing trade finance, lowering costs and expanding reach. Adopting FinTech platforms and blockchain introduces new degrees of transparency, efficiency, and accessibility. For example, digital verification of trade documents and automated compliance checks cut processing times and reduce fraud, making international trade simpler and safer—even for smaller companies.
Emerging technologies will continue to play a key role in addressing the finance gap by expanding access to underserved regions and populations, ultimately making international trade more democratic and vibrant.
Final Thoughts
Trade finance is vital for bridging the global commerce’s inherent cash flow gap. Whether through traditional banking products or the latest digital infrastructure, trade finance underpins trust and liquidity in global supply chains. Buyers and sellers can mitigate risks, manage working capital, and seize new opportunities in international markets by drawing on tailored solutions. With continued innovation and concerted efforts to close the finance gap, businesses of all sizes have a pathway to long-term growth and resilience in the evolving world of global trade.