Pad printing has emerged as a vital innovation in the world of modern product design, fundamentally changing how brands approach artwork placement and surface branding. Its distinctive capability to deliver crisp, intricate graphics on objects with challenging shapes has established pad printing as an integral aspect of various manufacturing processes. Numerous companies now rely on pad printing equipment to achieve unparalleled accuracy, efficiency, and quality, regardless of the substrate or shape involved. As product designers explore new frontiers, pad printing offers creative freedom while ensuring durability and brand consistency.
This article examines how advances in pad printing not only enhance the aesthetics of consumer products but also improve their usability and longevity. By examining key trends and real-world applications, we uncover why pad printing stands at the forefront of both industrial and artistic innovation. Harnessing this technology enables industries to transcend traditional limitations, meeting the growing demand for customization and robust performance in sectors ranging from electronics to automotive and medical devices.
Understanding Pad Printing
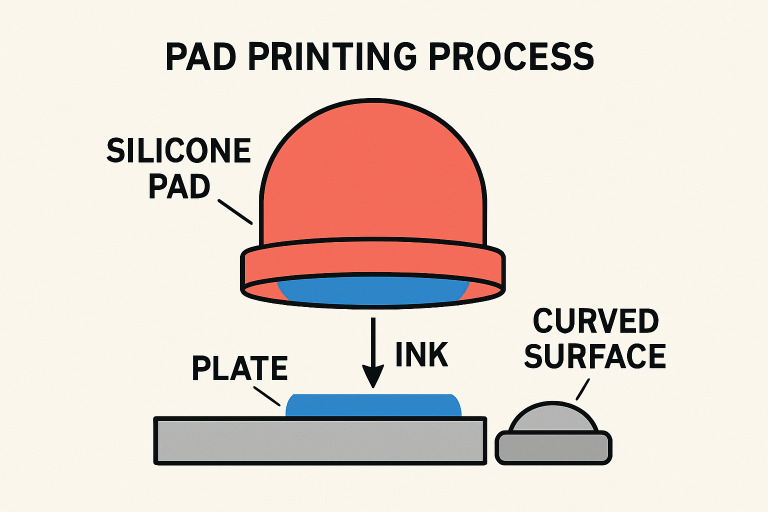
Pad printing, also known as tampography, is a sophisticated indirect offset printing process that utilizes a silicone pad to transfer 2D images onto uneven or complex 3D surfaces. At its core, the process begins with an etched plate filled with ink. The flexible silicone pad picks up the inked image and then carefully deposits it onto the product surface, accommodating design elements even on concave, convex, or textured substrates. This adaptability makes pad printing ideal for printing on plastics, metals, glass, and ceramics, as well as for products that require precise, multi-colored markings or intricate patterns.
Compared to other printing methods, pad printing stands out for its ability to consistently print fine details and microtext—an advantage crucial for industries with tight regulatory requirements, such as electronics and medical devices. As manufacturers pursue sophisticated branding and product differentiation in a crowded market, pad printing unlocks new creative possibilities while adhering to strict standards. Scientific resources such as ScienceDirect highlight how this approach maintains exceptional image fidelity even under mass-production constraints.
Advancements in Pad Printing Technology
The evolution of pad printing is a testament to modern engineering. Key innovations have propelled the process forward, from the introduction of laser-engraved plates—which ensure crisp etching, minimal wear, and rapid changeovers—to the convergence of digital inkjet technology. With these hybrid systems, designers can now produce photo-realistic color gradients and fine graphics that were once impossible with analog pads alone.
Improved machine automation has further reduced waste and downtime, enabling swift adjustments and batch customization. Industry reports indicate that these technical advancements are driving substantial market growth, with the global pad printing machine sector projected to exceed $1.8 billion by 2032. Automated ink management and precision pads also enhance efficiency, ensuring cost-effective and high-quality outputs that meet the expanding demands of global markets.
Applications Across Industries
The practical utility of pad printing stretches across every major manufacturing sector:
- Automotive: Interior button panels, dashboard branding, and safety icons rely on resilient, visually consistent pad prints for functionality and aesthetics.
- Electronics: Smartphones, keyboards, and remotes require crisp, wear-resistant logos and control labeling, which pad printing delivers over curves and angles.
- Medical Devices: Regulatory-mandated markings on surgical tools and instruments depend on the process’s durability, ensuring clarity after repeated use and sterilization cycles.
Pad printing is also increasingly utilized in sporting goods, toys, home appliances, and promotional items, where flexibility, accuracy, and durability are highly valued attributes.
Enhancing Product Aesthetics and Functionality
The influence of pad printing goes beyond surface decoration—its ability to introduce user-centric iconography and detailed visual cues directly onto designed components transforms product interaction. Take, for instance, the automotive sector, where high-contrast, clear icons and tactile surfaces support safer, more intuitive user experiences. For consumer electronics, premium brands count on the technology for long-lasting branding and compliant markings that won’t fade under heavy handling or cleaning.
Even in cost-sensitive industries or where utility is key, pad printing elevates perceived product value. The exactness of prints conveys a sense of craftsmanship and attention to detail, setting brands apart in fiercely competitive spaces while also helping them comply with regulatory demands. These benefits underscore why pad printing isn’t just a technical step but a true partner in industrial design.
Sustainability in Pad Printing
As climate concerns grow, manufacturers are vigorously adopting responsible practices. Pad printing leads in this area by enabling the use of solvent-free and low-volatile organic compound (VOC) inks, along with recyclable and reusable components. Laser-engraved plates significantly reduce consumable waste and energy, contributing to the effort to minimize the carbon footprint of industrial production.
Modern machines also feature energy-conserving designs and highly efficient ink transfer processes, thereby reducing environmental impact without compromising print quality or speed. These improvements are pivotal as companies align their operations with the EPA’s sustainability recommendations and the broader shift towards greener manufacturing frameworks.
Future Trends in Pad Printing
Pad printing is poised for an era of intelligent automation and digital convergence. Developments in programmable robotics, vision systems, and artificial intelligence will drastically enhance accuracy, repeatability, and productivity. AI-enabled machines may soon offer real-time error correction, predictive maintenance, and end-to-end print process optimization, thereby reducing lead times and the cost per print.
Material science breakthroughs will further expand the scope of pad printing, introducing new ink chemistries and substrates suitable for extreme environments or lightweight applications. As the customization trend continues, expect pad printing to play a key role in on-demand manufacturing, supporting everything from limited-edition gadgets to tailored healthcare devices.
Conclusion
Pad printing technology is redefining what is possible in product design and manufacturing. With its unique ability to decorate, brand, and functionalize virtually any surface, it delivers a winning combination of efficiency, precision, and sustainability. As new advancements emerge and industries continue to prioritize distinctiveness and environmental stewardship, pad printing’s role will only grow—solidifying its position at the heart of innovative, modern product development.